作为个人学习笔记分享,有任何问题欢迎交流!
Note:若是想要用pdb调试OpenStack,必须通过Devstack安装它。
Devstack安装Havana过程
1. 使用一般用户(非root用户),从github上获取devstack代码
git clonehttps://github.com/openstack-dev/devstack.git
2. 使用一般用户运行
cd devstack; ./stack.sh
(参考:)
3.安装过程中要求输入一些密码,这些密码将记录在localrc文件中,该文件还可以用来配置安装的openstack组件,默认的只会安装glance,keystone,nova,horizon.
4. 创建文件creds:
exportSERVICE_TOKEN=xxx(3中输入的密码)
exportOS_TENANT_NAME=admin
exportOS_USERNAME=admin
export OS_PASSWORD=xxx
exportOS_AUTH_URL=http://localhost:5000/v2.0/
exportSERVICE_ENDPOINT=http://localhost:35357/v2.0
source creds就可以使用openstack了
5. 若想更改已安装的组件,再./stack.sh即可
Pdb调试Havana过程
1. 修改代码
在需要调试的地方加入:
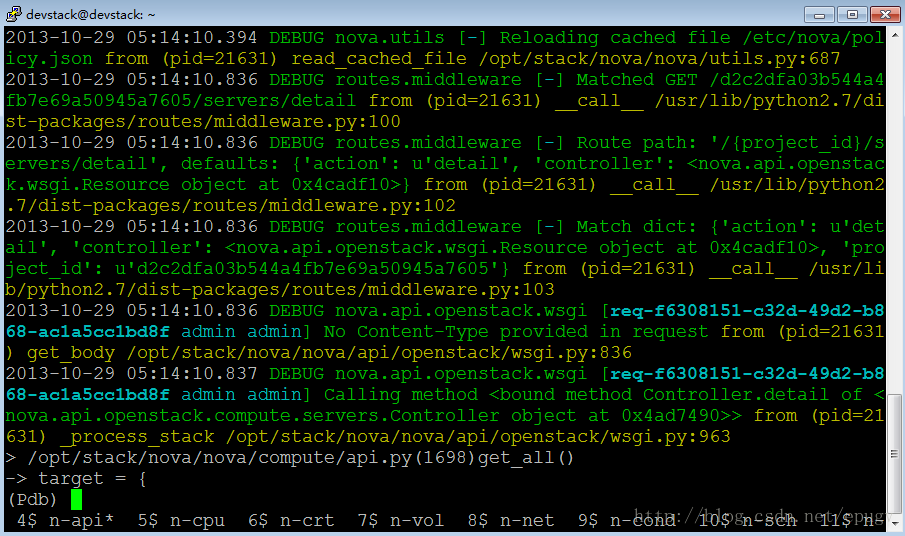
import pdb; pdb.set_trace()(以在nova/compute/api.py:get_all()中加入pdb为例)
2. 使用附录上的脚步restart_stack.sh重启服务(该脚本只针对默认安装的组件有效)
3. 开始调试:
显示有两个screen
screen –x stack
进入如下界面:
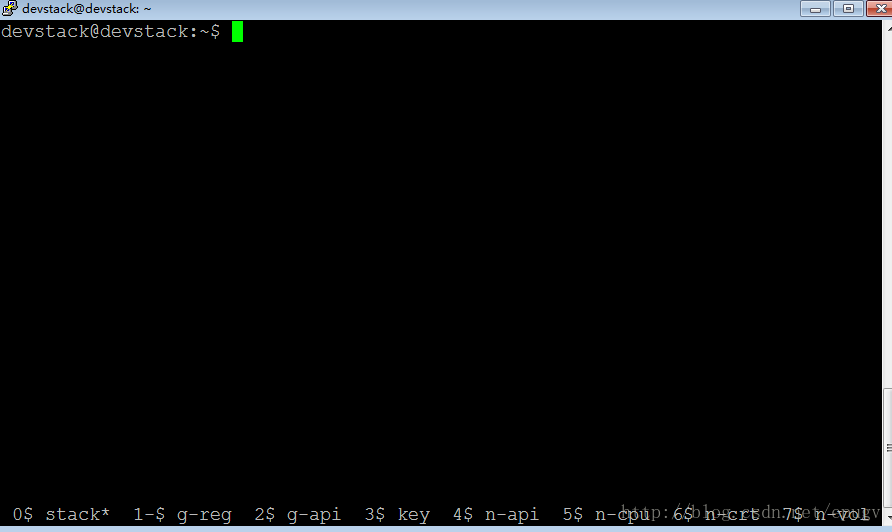
最下一行表示,每一个进程都有一个screen。带*号的表示当前的screen,可以同时按下ctrl+a+8和ctrl+a+2分别前进和后退,来切换不同的screen.
4. 在0$中输入nova list;切换到4$ n-api:
5. 开始使用pdb进行调试
注意问题
1. 在./restart_stack后,如果某个服务一直在waiting,说明这个服务运行到了你设置的断点,那么可以使用ctrl+z,把当前的进行切换到后台,然后screen –x stack,找到该服务对应的窗口进行调试,如果不需要在服务启动时就进行调试的话,按‘c’,让它继续执行。之后Ctrl+a +d退出screen,用jobs命令查看后台运行的进程,fg+进程ID, 就可以把./restart_stack.sh的后台进程调出来继续执行了。
2. ./restart_stack后,Horizon使用不了。
参考资料
1.
2.
附录
###########restart_stack.sh#########################!/usr/bin/env bash#restart the interfaces#sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart# close previrous screenSCREEN=$(which screen)if [[ -n "$SCREEN" ]]; then SESSION=$(screen -ls | awk '/[0-9].stack/ { print $1 }') if [[ -n "$SESSION" ]]; then echo "close session: $SESSION" echo "" screen -X -S $SESSION quit fifiTOP_DIR=$(cd $(dirname "$0") && pwd)# create a new named screen to run processes inscreen -d -m -S stack -t stack -s /bin/bashsleep 1# set a reasonable statusbarif [ -z "$SCREEN_HARDSTATUS" ]; then SCREEN_HARDSTATUS='%{= .} %-Lw%{= .}%> %n%f %t*%{= .}%+Lw%< %-=%{g}(%{d}%H/%l%{g})'fiscreen -r stack -X hardstatus alwayslastline "$SCREEN_HARDSTATUS"SERVICE_TIMEOUT=${SERVICE_TIMEOUT:-60}# Specify which services to launch. These generally correspond to# screen tabs. If you like to add other services that are not enabled# by default you can append them in your ENABLED_SERVICES variable in# your localrc. For example for swift you can just add this in your# localrc to add it with the other services:# ENABLED_SERVICES="$ENABLED_SERVICES,swift"ENABLED_SERVICES=g-api,g-reg,key,n-api,n-crt,n-obj,n-cpu,n-net,n-cond,n-vol,n-sch,n-novnc,n-xvnc,n-cauth,horizon,mysql,rabbit# is_service_enabled() checks if the service(s) specified as arguments are# enabled by the user in **ENABLED_SERVICES**.## If there are multiple services specified as arguments the test performs a# boolean OR or if any of the services specified on the command line# return true.## There is a special cases for some 'catch-all' services::# **nova** returns true if any service enabled start with **n-**# **glance** returns true if any service enabled start with **g-**# **neutron** returns true if any service enabled start with **q-**function is_service_enabled() { services=$@ for service in ${services}; do [[ ,${ENABLED_SERVICES}, =~ ,${service}, ]] && return 0 [[ ${service} == "nova" && ${ENABLED_SERVICES} =~ "n-" ]] && return 0 [[ ${service} == "glance" && ${ENABLED_SERVICES} =~ "g-" ]] && return 0 [[ ${service} == "neutron" && ${ENABLED_SERVICES} =~ "q-" ]] && return 0 done return 1}DEST=${DEST:-/opt/stack}# Set the destination directories for openstack projectsNOVA_DIR=$DEST/novaHORIZON_DIR=$DEST/horizonGLANCE_DIR=$DEST/glanceGLANCECLIENT_DIR=$DEST/python-glanceclientKEYSTONE_DIR=$DEST/keystoneNOVACLIENT_DIR=$DEST/python-novaclientKEYSTONECLIENT_DIR=$DEST/python-keystoneclientOPENSTACKCLIENT_DIR=$DEST/python-openstackclientNOVNC_DIR=$DEST/noVNCSWIFT_DIR=$DEST/swiftSWIFT3_DIR=$DEST/swift3NEUTRON_DIR=$DEST/neutronNEUTRON_CLIENT_DIR=$DEST/python-neutronclientMELANGE_DIR=$DEST/melangeMELANGECLIENT_DIR=$DEST/python-melangeclient# By default the location of swift drives and objects is located inside# the swift source directory. SWIFT_DATA_DIR variable allow you to redefine# this.SWIFT_DATA_DIR=${SWIFT_DATA_DIR:-${DEST}/data/swift}# We are going to have the configuration files inside the source# directory, change SWIFT_CONFIG_DIR if you want to adjust that.SWIFT_CONFIG_DIR=${SWIFT_CONFIG_DIR:-/etc/swift}# devstack will create a loop-back disk formatted as XFS to store the# swift data. By default the disk size is 1 gigabyte. The variable# SWIFT_LOOPBACK_DISK_SIZE specified in bytes allow you to change# that.SWIFT_LOOPBACK_DISK_SIZE=${SWIFT_LOOPBACK_DISK_SIZE:-1000000}# The ring uses a configurable number of bits from a path聮s MD5 hash as# a partition index that designates a device. The number of bits kept# from the hash is known as the partition power, and 2 to the partition# power indicates the partition count. Partitioning the full MD5 hash# ring allows other parts of the cluster to work in batches of items at# once which ends up either more efficient or at least less complex than# working with each item separately or the entire cluster all at once.# By default we define 9 for the partition count (which mean 512).SWIFT_PARTITION_POWER_SIZE=${SWIFT_PARTITION_POWER_SIZE:-9}# This variable allows you to configure how many replicas you want to be# configured for your Swift cluster. By default the three replicas would need a# bit of IO and Memory on a VM you may want to lower that to 1 if you want to do# only some quick testing.SWIFT_REPLICAS=${SWIFT_REPLICAS:-3}if is_service_enabled swift; then # If we are using swift, we can default the s3 port to swift instead # of nova-objectstore S3_SERVICE_PORT=${S3_SERVICE_PORT:-8080}fi# Set default port for nova-objectstoreS3_SERVICE_PORT=${S3_SERVICE_PORT:-3333}# Set the tenant for service accounts in KeystoneSERVICE_TENANT_NAME=${SERVICE_TENANT_NAME:-service}HOST_IP_IFACE=${HOST_IP_IFACE:-eth0}# Use the eth0 IP unless an explicit is set by ``HOST_IP`` environment variableif [ -z "$HOST_IP" -o "$HOST_IP" == "dhcp" ]; then HOST_IP=`LC_ALL=C /sbin/ifconfig ${HOST_IP_IFACE} | grep -m 1 'inet addr:'| cut -d: -f2 | awk '{print $1}'` if [ "$HOST_IP" = "" ]; then echo "Could not determine host ip address." echo "Either localrc specified dhcp on ${HOST_IP_IFACE} or defaulted to eth0" exit 1 fifiSERVICE_HOST=${SERVICE_HOST:-$HOST_IP}# Glance connection info. Note the port must be specified.GLANCE_HOSTPORT=${GLANCE_HOSTPORT:-$SERVICE_HOST:9292}# Set Keystone interface configurationKEYSTONE_API_PORT=${KEYSTONE_API_PORT:-5000}KEYSTONE_AUTH_HOST=${KEYSTONE_AUTH_HOST:-$SERVICE_HOST}KEYSTONE_AUTH_PORT=${KEYSTONE_AUTH_PORT:-35357}KEYSTONE_AUTH_PROTOCOL=${KEYSTONE_AUTH_PROTOCOL:-http}KEYSTONE_SERVICE_HOST=${KEYSTONE_SERVICE_HOST:-$SERVICE_HOST}KEYSTONE_SERVICE_PORT=${KEYSTONE_SERVICE_PORT:-5000}KEYSTONE_SERVICE_PROTOCOL=${KEYSTONE_SERVICE_PROTOCOL:-http}# Our screenrc file builderfunction screen_rc { SCREENRC=$TOP_DIR/stack-screenrc if [[ ! -e $SCREENRC ]]; then # Name the screen session echo "sessionname stack" > $SCREENRC # Set a reasonable statusbar echo "hardstatus alwayslastline '$SCREEN_HARDSTATUS'" >> $SCREENRC echo "screen -t stack bash" >> $SCREENRC fi # If this service doesn't already exist in the screenrc file if ! grep $1 $SCREENRC 2>&1 > /dev/null; then NL=`echo -ne '\015'` echo "screen -t $1 bash" >> $SCREENRC echo "stuff \"$2$NL\"" >> $SCREENRC fi}# Our screen helper to launch a service in a hidden named screenfunction screen_it { NL=`echo -ne '\015'` if is_service_enabled $1; then echo Starting $1 ... # Append the service to the screen rc file screen_rc "$1" "$2" screen -S stack -X screen -t $1 # sleep to allow bash to be ready to be send the command - we are # creating a new window in screen and then sends characters, so if # bash isn't running by the time we send the command, nothing happens sleep 1.5 if [[ -n ${SCREEN_LOGDIR} ]]; then screen -S stack -p $1 -X logfile ${SCREEN_LOGDIR}/screen-${1}.${CURRENT_LOG_TIME}.log screen -S stack -p $1 -X log on ln -sf ${SCREEN_LOGDIR}/screen-${1}.${CURRENT_LOG_TIME}.log ${SCREEN_LOGDIR}/screen-${1}.log fi screen -S stack -p $1 -X stuff "$2$NL" fi}GLANCE_CONF_DIR=/etc/glance# launch the glance registry serviceif is_service_enabled g-reg; then screen_it g-reg "cd $GLANCE_DIR; /usr/local/bin/glance-registry --config-file=$GLANCE_CONF_DIR/glance-registry.conf"fi# launch the glance api and wait for it to answer before continuingif is_service_enabled g-api; then screen_it g-api "cd $GLANCE_DIR; /usr/local/bin/glance-api --config-file=$GLANCE_CONF_DIR/glance-api.conf" echo "Waiting for g-api ($GLANCE_HOSTPORT) to start..." if ! timeout $SERVICE_TIMEOUT sh -c "while ! http_proxy= wget -q -O- http://$GLANCE_HOSTPORT; do sleep 1; done"; then echo "g-api did not start" exit 1 fifiif is_service_enabled key; then KEYSTONE_CONF_DIR=${KEYSTONE_CONF_DIR:-/etc/keystone} KEYSTONE_CONF=$KEYSTONE_CONF_DIR/keystone.conf KEYSTONE_CATALOG=$KEYSTONE_CONF_DIR/default_catalog.templates # Set up logging LOGGING_ROOT="devel" if [ "$SYSLOG" != "False" ]; then LOGGING_ROOT="$LOGGING_ROOT,production" fi KEYSTONE_LOG_CONFIG="--log-config $KEYSTONE_CONF_DIR/logging.conf" # launch keystone and wait for it to answer before continuing screen_it key "cd $KEYSTONE_DIR && $KEYSTONE_DIR/bin/keystone-all --config-file $KEYSTONE_CONF $KEYSTONE_LOG_CONFIG -d --debug" echo "Waiting for keystone to start..." if ! timeout $SERVICE_TIMEOUT sh -c "while ! http_proxy= wget -O- $KEYSTONE_AUTH_PROTOCOL://$SERVICE_HOST:$KEYSTONE_API_PORT/v2.0/ 2>&1 | grep -q '200 OK'; do sleep 1; done"; then echo "keystone did not start" exit 1 fifi# launch the nova-api and wait for it to answer before continuingif is_service_enabled n-api; then screen_it n-api "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-api" echo "Waiting for nova-api to start..." if ! timeout $SERVICE_TIMEOUT sh -c "while ! http_proxy= wget -q -O- http://127.0.0.1:8774; do sleep 1; done"; then echo "nova-api did not start" exit 1 fifi# Launching nova-compute should be as simple as running ``nova-compute`` but# have to do a little more than that in our script. Since we add the group# ``libvirtd`` to our user in this script, when nova-compute is run it is# within the context of our original shell (so our groups won't be updated).# Use 'sg' to execute nova-compute as a member of the libvirtd group.# We don't check for is_service_enable as screen_it does it for usscreen_it n-cpu "cd $NOVA_DIR && sg libvirtd /usr/local/bin/nova-compute"screen_it n-crt "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-cert"screen_it n-vol "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-volume"screen_it n-net "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-network"screen_it n-cond "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-conductor"screen_it n-sch "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-scheduler"screen_it n-novnc "cd $NOVNC_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-novncproxy --config-file $NOVA_CONF_DIR/$NOVA_CONF --web ."screen_it n-xvnc "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-xvpvncproxy --config-file $NOVA_CONF_DIR/$NOVA_CONF"screen_it n-cauth "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-consoleauth"screen_it horizon "cd $HORIZON_DIR && sudo tail -f /var/log/$APACHE_NAME/horizon_error.log"screen_it swift "cd $SWIFT_DIR && $SWIFT_DIR/bin/swift-proxy-server ${SWIFT_CONFIG_DIR}/proxy-server.conf -v"# Starting the nova-objectstore only if swift service is not enabled.# Swift will act as s3 objectstore.is_service_enabled swift || \ screen_it n-obj "cd $NOVA_DIR && /usr/local/bin/nova-objectstore"